Introduction
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) are becoming increasingly prevalent in various aspects of our lives. These technologies, which blend the physical and digital worlds, have the potential to revolutionize industries such as healthcare, education, entertainment, and more. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and it is essential to explore the ethical implications of AR and MR to ensure that their integration into society is beneficial and fair.
Definition
Through the use of smartphones or AR glasses, augmented reality (AR) superimposes digital content on the physical world to improve perception. In order to enable engagement and immersion beyond augmented reality, mixed reality (MR) incorporates virtual aspects into the real world. The digital and physical worlds are combined by these technologies to provide a variety of applications for training, education, and gaming.
Privacy Concerns
One of the most pressing ethical issues surrounding AR and MR is privacy. These technologies often rely on collecting and processing vast amounts of data. To create immersive experiences. For example, AR applications can use cameras to overlay digital information onto the real world. While MR systems can track users’ movements and interactions within a mixed reality environment. This data collection raises several concerns:
- Surveillance: The continuous monitoring required for AR and MR can lead to a sense of being constantly watched, which can infringe on personal privacy.
- Data Security: The data collected by AR and MR devices, such as location information, biometric data, and user preferences, must be securely stored and protected from breaches.
- Consent: Users must be fully informed about what data is being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it. Obtaining explicit consent is crucial.
Psychological and Social Impact
AR and MR have the potential to alter the way we perceive and interact with the world. Which can have significant psychological and social implications. While these technologies can enhance our experiences, they also come with risks:
- Reality Distortion: The blending of digital and physical realities can blur the lines between them. What is real and what is virtual, potentially leading to confusion or a distorted sense of reality.
- Addiction: The immersive nature of AR and MR can make them highly engaging. Which may lead to excessive use and addiction, particularly among younger users.
- Social Isolation: While AR and MR can facilitate new forms of social interaction. They Can also contribute to social isolation if users prefer virtual interactions over real-life connections.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Ensuring that AR and MR technologies are accessible and inclusive is another critical ethical consideration. As these technologies become more widespread. It is essential to address the following issues:
- Digital Divide: There is a risk that AR and MR could exacerbate the digital divide. As not everyone has equal access to the necessary devices and infrastructure.
- Usability: AR and MR applications must be designed with a diverse user base in mind. Including individuals with disabilities. This includes considering factors such as visual, auditory, and motor impairments.
- Affordability: The cost of AR and MR devices and applications should be reasonable. To prevent economic barriers from limiting access to these technologies.
Impact on Employment
The integration of AR and MR into various industries can have significant implications for employment. While these technologies can create new job opportunities and improve productivity, they may also lead to job displacement:
- Job Creation: AR and MR can generate demand for new roles in development, maintenance and support of these technologies.
- Job Displacement: Automation and enhanced efficiency brought about by AR and MR may render certain jobs obsolete. And leading to unemployment and economic disruption.
- Reskilling: There is a need for initiatives to help workers. To adapt changes in the job market by providing training and education in new skills relevant to AR and MR.
Ethical Use in Education
By enabling immersive and dynamic learning environments. AR and MR have enormous potential to revolutionise education. However, ethical considerations must be addressed to ensure their responsible use in educational settings:
- Content Accuracy: The information presented through AR and MR must be accurate and reliable. To prevent the dissemination of misinformation.
- Equity in Education: Ensuring that all students have equal access to AR and MR technologies is essential. To prevent disparities in educational opportunities.
- Teacher Training: Educators must be adequately trained to effectively integrate AR and MR into their teaching methods while addressing potential ethical issues.
Ethical Marketing and Advertising
The use of AR and MR in marketing and advertising also raises ethical questions. These technologies can create highly engaging and persuasive advertisements, but there are concerns about:
- Manipulation: AR and MR ads can be designed to be highly immersive and persuasive, potentially manipulating consumers’ perceptions and behaviors.
- Transparency: Advertisements using AR and MR should be clearly identifiable as such to avoid misleading consumers.
- Data Collection: The use of AR and MR in marketing often involves collecting data on consumer preferences and behaviors, raising concerns about privacy and data security.
Intellectual Property and Content Ownership
The creation and use of digital content in AR and MR environments bring about issues related to intellectual property and content ownership:
- Copyright Infringement: The ease of creating and sharing digital content in AR and MR can lead to unauthorized use of copyrighted materials.
- Ownership Rights: Clarifying who owns the content created within AR and MR environments is essential, particularly in collaborative or user-generated contexts.
- Fair Use: Establishing guidelines for the fair use of digital content in AR and MR applications is necessary to balance the interests of creators and users.
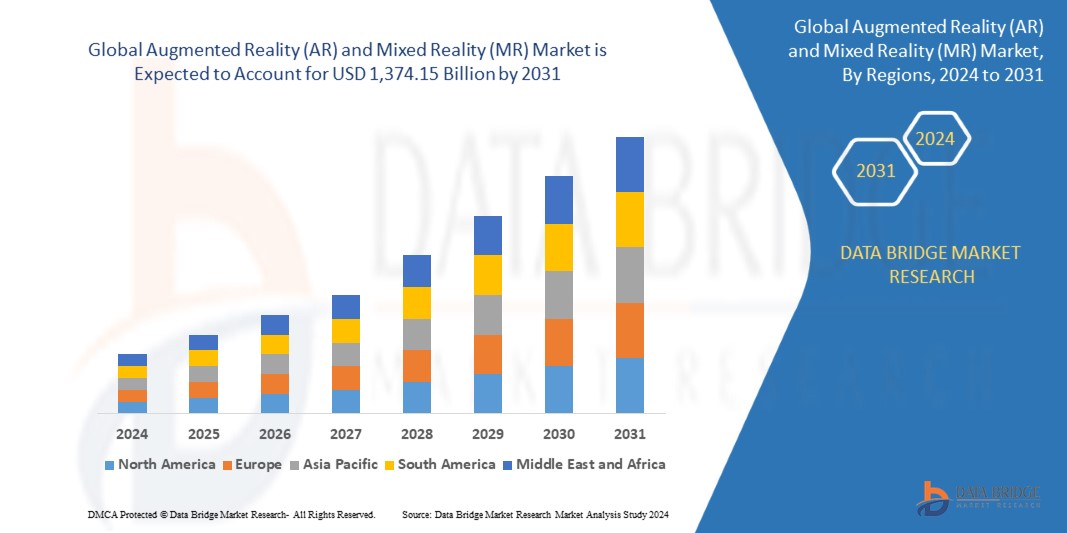
Growth Rate of Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) Market
The market for Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) was estimated to be worth USD 52.21 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 50.5% to reach USD 1,374.15 billion by 2031.
Conclusion
The ethical implications of Augmented Reality and Mixed Reality are complex and multifaceted. It is imperative that we proactively address these ethical problems as these technologies continue to progress and become increasingly incorporated into our daily lives. By doing so, we can harness the potential of AR and MR to enhance our experiences while ensuring that their use is fair, responsible, and beneficial for all members of society. Engaging in ongoing dialogue and developing robust ethical frameworks will be key to navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by these transformative technologies.
Leave a Reply